Next: 4 Top Level command Program Architecture Up: Appnotes Index Previous:2 Introduction
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: 4 Top Level command Program Architecture
Up: Appnotes Index
Previous:2 Introduction
Processing System into the Air-to-Ground mapping state. Since the CP also speaks this state oriented language it may be viewed as part of the CCS. Control a Signal Processing Program that has been graphically specified via a dataflow model of computation and autocoded, a generic set of controls over the signal processing graphs are made available to the CP. They define the complete set of commands understood by the signal processing program. (See the Data Flow Graph application note for a complete discussion of these capabilities.) The abilities provided fall into several broad categories:
Depending on real-time conditions, some data-flow may need to be rerouted either within a graph or among distinct graphs and is therefore also under the control
of the CP. It is important to emphasize that most data-flow is not under control of the CP. That which is under CP control is used to perform infrequent,
significant graph reconfigurations. The CP may manage data-flow within a graph by simply setting parameters controlling "switches" in the graph. Data flowing
between distinct graph instances may be managed by connecting and disconnecting dynamic queues serving as pipes between the graphs. The CP can also be
connected via dynamic queues to the signal processing program. Typically the data read/written on these queues is low rate.
3.0 What is a Command Program
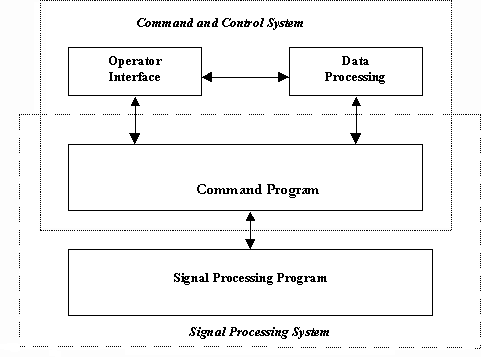
A typical large-scale embedded signal processing architecture consists of a signal processing system communicating with a command and control system. The
signal processing system performs the high-bandwidth numerical processing and typically executes on Digital Signal Processors (DSPs). It is controlled by a
command program (CP) that is intimately related to the signal processing system. The command program serves as an interface between the signal processing
program and the rest of the command and control system. This is done by translating system-derived or user provided inputs into commands understood by the
signal processing system. The results processed by the signal processing system are then fed back to the command and control system.
The command program serves as an interface between the signal processing program and the rest of the command and control system. This is done by translating
system-derived or user provided inputs into commands understood by the signal processing system. The results processed by the signal processing system are
then fed back to the command and control system.
Figure 3 - 1, A Typical Large Scale Aerospace Architecture, shows the command program ambiguously residing in both the Signal Processing System and the
Command and Control System. The generic controls over the signal processing program all reflect the graphical structure of that program, and thus the CP is
frequently conceptualized as a part of the Signal Processing System. But this is only half of the story. The CP receives commands and forwards results to the
Command and Control System, which is unaware of the graph structure of the Signal Processing System. This communication between the CP and the rest of the
Command and Control System (CCS) occurs in the "language" of the CCS which usually is state oriented. For example the CCS may want to place an Airborne
Radar Signal
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: 4 Application Example
Up: Appnotes Index
Previous:2 Introduction