There are three types of timing control, delay based, event based and level sensitive. We will discuss the useful aspects of each in turn.
Syntax:
timing_control_statement::==
delay_based
statement*
delay_based::==
#
delay_value
This method introduces a delay between when a statement is encountered and when it is executed.
initial begin
a = 0; // executed at simulation time 0
#10 b = 2; // executed at simulation time 10
#15 c = a; // ... at time 25
#b c = 4; // ... at time 27
b=5; // ... at time 27
end
initial begin
clock = 1'b0;
forever #5 clock = ~clock;
end
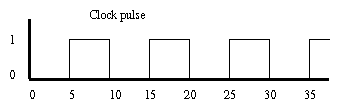
This will make the clock flip every 5 time units giving a wave form as shown.
EXERCISE
In the following module what would be the values of
a) a at time 15 units;
b) b at 17 units
c) c at 18 units
d) a at 30 units
module testdelay(a, b, c);
output [3:0] a, b, c;
reg [3:0] a, b, c;
initial begin
#10 a = 3;
#5 b = 4;
#6 c = 5;
#8 a = a + b;
end
endmodule